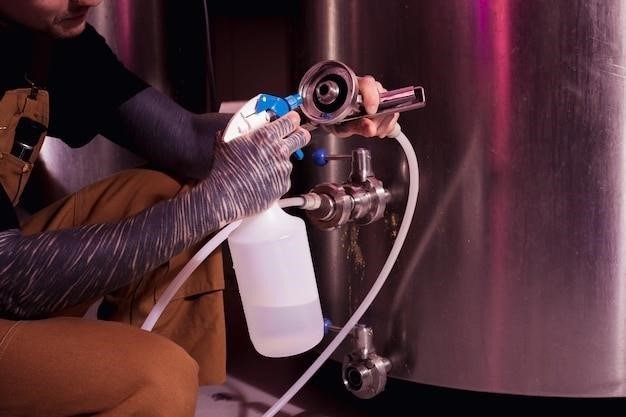
Manual Bottle Filling Equipment⁚ A Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of manual bottle filling equipment, covering its types, advantages, disadvantages, applications, and factors to consider when choosing the right equipment for your needs․ We’ll delve into volumetric and gravity filling methods, explore maintenance, safety considerations, and conclude with valuable resources for further information․
Introduction
Manual bottle filling equipment plays a crucial role in various industries, from small-scale operations to larger production lines․ These machines offer a cost-effective and efficient solution for filling bottles with liquids, pastes, and other products․ Manual bottle fillers are particularly well-suited for businesses that require low production volumes, have limited space, or are starting out and need a simple, affordable solution․ Unlike automated filling systems, manual bottle fillers require human intervention for each bottle, making them ideal for smaller batches and specialized applications․
The versatility of manual bottle filling equipment is evident in its wide range of applications, encompassing industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, chemicals, and more․ From filling small vials with essential oils to larger containers with liquids, manual bottle fillers provide a reliable and precise method for packaging various products․ The simplicity of operation and ease of maintenance make them attractive for hobbyists, small businesses, and even larger companies seeking flexibility and cost-effectiveness in their production processes․
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of manual bottle filling equipment, exploring its different types, advantages, disadvantages, applications, and factors to consider when choosing the right equipment for your specific needs․ We will also discuss maintenance, safety considerations, and valuable resources for further information․
Types of Manual Bottle Filling Equipment
Manual bottle filling equipment encompasses a variety of designs and mechanisms, each tailored to specific applications and product types․ The most common types include⁚
- Volumetric Filling Machines⁚ These machines utilize a precise volume of liquid dispensed into each bottle․ They often feature a piston or cylinder mechanism, allowing for accurate and repeatable filling․ Volumetric fillers are ideal for products that require consistent dosage, such as pharmaceuticals or cosmetics․
- Gravity Filling Machines⁚ Gravity filling relies on the natural force of gravity to fill bottles․ Liquid is stored in a reservoir above the bottles, and as it flows down through a nozzle, it fills the container․ This method is suitable for products with low viscosity and those that don’t require high precision in filling levels․
- Peristaltic Filling Machines⁚ These machines use a flexible tube to pump liquid into the bottles․ A rotating roller compresses the tube, creating a peristaltic action that moves the liquid forward․ Peristaltic fillers are known for their gentle handling, minimizing product damage and ensuring accurate filling․
- Paste Filling Machines⁚ Designed for thick, viscous products like creams, gels, and pastes, these machines often incorporate a piston or screw mechanism to push the product into the bottle․ Paste fillers ensure consistent and controlled filling, even for challenging materials․
The choice of manual bottle filling equipment depends on factors like product type, desired filling accuracy, production volume, and budget․ It is essential to carefully evaluate each type’s advantages and disadvantages to select the most suitable option for your specific needs․
Volumetric Filling
Volumetric filling is a precise method that utilizes a pre-determined volume of liquid for each bottle․ This technique is commonly employed in manual bottle filling machines, offering accuracy and repeatability in dispensing․
The core principle of volumetric filling relies on a piston or cylinder mechanism within the machine․ Liquid is drawn into a chamber, and a piston or plunger then accurately displaces the measured volume into the bottle․
Key advantages of volumetric filling include⁚
- Accuracy⁚ Volumetric filling ensures consistent and precise liquid dispensing, minimizing variations between bottles․ This is crucial for products requiring accurate dosage, such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food additives․
- Repeatability⁚ The pre-determined volume eliminates the need for constant adjustments, ensuring consistent filling across production runs․ This contributes to product uniformity and quality control․
- Efficiency⁚ Volumetric filling is generally a quick process, allowing for efficient production even with manual operation․ The pre-measured volume reduces the need for manual adjustments, streamlining the filling process․
However, volumetric filling also has some limitations⁚
- Product Viscosity⁚ Volumetric filling is most suitable for liquids with moderate viscosity․ Thick or highly viscous products may require specialized equipment or adjustments to ensure accurate filling․
- Container Size Variability⁚ Volumetric filling machines are designed for specific bottle sizes․ Significant variations in bottle size or shape can lead to inconsistencies in filling levels․
In summary, volumetric filling is a reliable and accurate method for manual bottle filling, particularly for products demanding consistent dosage and precise dispensing․
Gravity Filling
Gravity filling leverages the natural force of gravity to dispense liquid into bottles․ This method is often employed in manual bottle filling systems, particularly for low-viscosity liquids, and it’s known for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness․
The process involves a reservoir or tank containing the liquid, which is elevated above the filling station․ The liquid flows through a tube or nozzle into the bottles positioned beneath the reservoir․ The filling level is typically controlled by a pre-determined height of the reservoir or by a stop valve that regulates the flow․
Gravity filling offers several advantages⁚
- Simplicity⁚ The system is relatively straightforward to set up and operate, requiring minimal specialized equipment․ This makes it an accessible option for smaller operations or hobbyists․
- Low Cost⁚ Gravity filling systems are generally less expensive than other filling methods, as they require minimal automation or complex machinery․
- Flexibility⁚ Gravity filling can be adapted to a range of bottle sizes and shapes, providing flexibility for product packaging․
However, gravity filling also presents certain limitations⁚
- Filling Accuracy⁚ Gravity filling can be less precise than other methods, especially for products with varying viscosities or when handling small volumes․ Variations in bottle size or liquid flow can lead to inconsistencies in filling levels․
- Product Viscosity⁚ Gravity filling is best suited for low-viscosity liquids․ Thick or viscous products may flow too slowly or unevenly, resulting in inaccurate filling․
- Filling Speed⁚ Gravity filling is often slower than other methods, as it relies on the natural flow rate of the liquid․ This can limit production capacity, especially for larger volumes․
In conclusion, gravity filling is a practical and economical choice for manual bottle filling, particularly for low-viscosity liquids and smaller production scales․ However, it’s crucial to consider its limitations in terms of accuracy and filling speed before implementing this method․
Advantages of Manual Bottle Filling Equipment
Manual bottle filling equipment offers several advantages, making it a suitable choice for certain production scenarios․ These benefits include⁚
- Low Initial Investment⁚ Manual filling machines are generally less expensive than automated or semi-automated systems, making them an attractive option for startups, small businesses, or hobbyists with limited capital․ This affordability allows for a more gradual investment into production equipment․
- Versatility⁚ Manual filling machines can be adapted to handle a wider range of bottle sizes and shapes compared to automated systems, which may be more specialized․ This versatility allows for greater flexibility in packaging various products․
- Ease of Operation⁚ Manual filling machines are typically user-friendly and require minimal training to operate․ This simplifies the learning curve for new operators, reducing the need for specialized personnel․
- Minimal Maintenance⁚ Manual filling machines often have fewer moving parts and require less intricate maintenance compared to automated systems; This reduces the need for frequent repairs and maintenance, leading to lower overall operating costs․
- Space Efficiency⁚ Manual filling machines are often compact and require less space than automated systems․ This makes them suitable for smaller production facilities with limited floor space․
- Flexibility for Small Batches⁚ Manual filling is ideal for producing small batches of products or for handling unique or specialty items․ This flexibility allows for adapting production to meet specific customer orders or niche markets․
In addition to these core advantages, manual filling systems offer a sense of control and direct involvement in the production process․ This can be particularly appealing for businesses that value hands-on quality assurance or that require a more personalized approach to filling․
However, it’s crucial to remember that these advantages are balanced by certain limitations, such as lower production speed and potential for human error, which will be discussed in the following section․
Disadvantages of Manual Bottle Filling Equipment
While manual bottle filling equipment offers certain advantages, it also comes with inherent drawbacks that must be carefully considered before making a decision․ These disadvantages include⁚
- Lower Production Speed⁚ Manual filling machines are significantly slower than automated or semi-automated systems․ This limitation can impact production capacity, especially when dealing with high-volume orders or tight deadlines․
- Potential for Human Error⁚ The manual nature of the filling process introduces the possibility of human error․ Inconsistent filling levels, spills, or contamination can occur if proper procedures are not strictly adhered to․
- Limited Accuracy⁚ Manual filling machines may lack the precision and consistency of automated systems, particularly when handling delicate products or requiring precise fill volumes․ This can lead to variations in product quality and potential waste․
- Labor Intensive⁚ Manual filling requires a dedicated workforce to operate the equipment and perform tasks like bottle placement, capping, and labeling․ This can increase labor costs and create potential bottlenecks in the production process․
- Less Scalable⁚ Manual filling systems are typically less scalable than automated systems․ Expanding production capacity can be challenging with manual equipment, as it may require significant additional labor or equipment․
- Ergonomic Considerations⁚ Manual filling can be physically demanding and repetitive, leading to potential ergonomic issues for operators․ This can impact employee health and productivity over time․
It’s essential to weigh these disadvantages against the advantages of manual filling to determine if it’s the right choice for your specific production needs․ If high production volumes, precision, or automation are critical, then exploring alternative filling systems may be more suitable․
Understanding these limitations allows for a more informed decision regarding the suitability of manual bottle filling equipment for your business․
Applications of Manual Bottle Filling Equipment
Manual bottle filling equipment finds its niche in a variety of applications, particularly where smaller production volumes, budget constraints, or specific product characteristics are primary considerations․ Some common applications include⁚
- Small-Scale Production⁚ Manual filling machines are ideal for hobbyists, startups, or small businesses with limited production needs․ They provide an affordable entry point into bottling operations without the high investment of automated systems․
- Specialty Products⁚ Manual filling is often suitable for niche products or those requiring careful handling․ Examples include artisanal food products, handcrafted cosmetics, or pharmaceuticals with specific filling requirements․
- Research and Development⁚ In research and development settings, manual filling allows for experimentation and small-scale production runs while testing new formulations or packaging designs․
- Limited Space⁚ Manual filling equipment typically has a smaller footprint than automated systems, making it suitable for facilities with limited space or for mobile operations․
- Short Production Runs⁚ For occasional or short-term production runs, manual filling can be a cost-effective solution․ It eliminates the need for a significant investment in automated equipment that may only be used infrequently․
- Viscous Products⁚ Manual filling machines are often used for filling viscous products like honey, sauces, or pastes, as they provide greater control over the filling process and minimize product damage․
- Packaging Prototyping⁚ Manual filling is helpful for prototyping packaging designs or experimenting with different bottle shapes or sizes before committing to larger-scale production runs․
The versatility of manual filling equipment makes it a valuable tool for a range of applications․ Whether you are a small-scale producer, a researcher, or a business with specific production needs, manual filling can offer a practical and cost-effective solution;
Factors to Consider When Choosing Manual Bottle Filling Equipment
Selecting the right manual bottle filling equipment is crucial for achieving efficient and accurate filling operations․ Several key factors should be considered to ensure the equipment meets your specific needs⁚

- Production Volume⁚ Determine the anticipated production volume․ Manual filling machines are generally suited for low to medium production runs․ If you anticipate significant volume increases, consider a semi-automatic or fully automated system․
- Product Type⁚ The nature of your product is critical․ Consider factors like viscosity, density, and whether the product is prone to foaming or sedimentation․ Choose equipment designed for handling your specific product type․
- Filling Accuracy⁚ Decide on the desired level of filling accuracy․ Volumetric filling machines offer precise control over fill volumes, while gravity-fed systems may have slightly less accuracy․
- Bottle Size and Shape⁚ The size and shape of your bottles will dictate the type of filling head and bottle handling system required․ Consider the equipment’s compatibility with your chosen bottle design․
- Budget⁚ Manual filling machines are generally more affordable than automated systems․ Set a realistic budget and research options within your price range․
- Space Requirements⁚ Consider the available space in your production area․ Manual filling equipment typically has a smaller footprint, but ensure it fits comfortably within your facility․
- Ease of Use and Maintenance⁚ Choose equipment that is user-friendly and requires minimal maintenance․ This will ensure smooth operations and minimize downtime․
- Safety Features⁚ Evaluate the safety features of the equipment․ Look for features like spill prevention, ergonomic design, and clear instructions to ensure a safe working environment․
- Materials of Construction⁚ The materials used in the construction of the filling machine are important․ Stainless steel is a common choice for its durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning․
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose manual bottle filling equipment that aligns with your production needs, budget, and safety requirements․ This will ensure efficient and reliable filling operations for your products․
Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning are crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of manual bottle filling equipment․ A well-maintained system operates smoothly, minimizes downtime, and delivers consistent filling accuracy․ Here’s a comprehensive guide to maintenance and cleaning practices⁚
- Daily Cleaning⁚ After each filling session, clean the filling heads, nozzles, and any other parts that come into contact with the product․ Use a mild detergent solution and warm water․ Rinse thoroughly to remove any residue․
- Weekly Cleaning⁚ Conduct a more thorough cleaning of the entire equipment, including the hopper, filling mechanism, and any other components․ Use a cleaning solution suitable for your product type and the materials of construction․ Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for cleaning agents․
- Periodic Lubrication⁚ Lubricate moving parts such as bearings, gears, and slides according to the manufacturer’s instructions․ Use the appropriate lubricant for the specific parts to ensure smooth operation and prevent wear․
- Inspection of Components⁚ Regularly inspect the filling heads, nozzles, hoses, and seals for any signs of wear, damage, or leaks․ Replace worn or damaged components promptly to prevent potential problems․
- Calibration⁚ Periodically calibrate the filling machine to ensure accurate fill volumes․ Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration procedures․
- Storage⁚ When not in use, store the equipment in a clean and dry environment to prevent corrosion and dust accumulation․ Cover the machine with a protective sheet to further protect it from dust and moisture․
- Documentation⁚ Maintain a record of maintenance activities, including cleaning dates, lubrication dates, and any component replacements․ This documentation will help track the equipment’s history and identify any recurring issues․
By implementing these maintenance and cleaning practices, you can ensure the long-term reliability and efficiency of your manual bottle filling equipment․ This will contribute to consistent product quality, reduced downtime, and a safe and hygienic production environment․
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount when operating manual bottle filling equipment․ While these machines are generally considered relatively safe, potential hazards exist that require careful attention and adherence to safety practices․ Here are some key safety considerations⁚
- Proper Training⁚ Ensure that all operators are adequately trained in the safe operation and maintenance of the equipment․ Training should cover operating procedures, potential hazards, safety precautions, and emergency response procedures․
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)⁚ Provide and require operators to wear appropriate PPE, such as safety glasses, gloves, and closed-toe shoes, to protect them from potential hazards like spills, splashes, and moving parts․
- Machine Guarding⁚ Ensure that all moving parts, such as filling heads, nozzles, and conveyors, are properly guarded to prevent accidental contact and injuries․
- Electrical Safety⁚ Inspect electrical cords and connections regularly for damage or wear․ Ensure that the equipment is properly grounded to prevent electrical shocks․
- Safe Handling of Products⁚ Exercise caution when handling the product being filled․ If the product is hazardous or corrosive, handle it with appropriate protective gear and follow safety protocols․
- Emergency Procedures⁚ Develop and clearly communicate emergency procedures for handling spills, accidents, or equipment malfunctions․ Ensure that all operators are aware of these procedures․
- Regular Inspections⁚ Conduct regular inspections of the equipment for any signs of wear, damage, or leaks․ Address any issues promptly to prevent potential hazards․
- Cleanliness⁚ Maintain a clean and organized work area to minimize the risk of slips, trips, and falls․ Regularly clean up spills and debris․
- Work Area Safety⁚ Ensure that the work area is well-lit and free of obstructions․ Provide adequate space for operators to move around safely․
By prioritizing safety and following these guidelines, you can create a safe and productive work environment for your manual bottle filling operations․
